Twitter Open Source Intelligence
Twitter is a great source for conducting open source intelligence. One of my favorite tools is Tweetsniff from Xavier Mertens. It will grab a Twitter user timeline for further processing, for example in Elasticsearch.
Another tool that I recently discovered is Tinfoleak. Tinfoleak is build for Twitter intelligence analysis and provides you with an HTML file output.
I wanted to use Tinfoleak to build profiles of users to tune targeted phishing campaigns (spear phishing) for a penetration test. For automated campaigns it would be easier if Tinfoleak can export to CSV but this engagement required a lot of manual labour anyway, so converting the HTML file to useful data for the campaign was not a big problem.
A big advantage of Tinfoleak is that it is easily available via a binary package in the Kali package repository.
apt-get install tinfoleak
A warning though : the package in the repository is an older (v2.1) version. The Github repository provides you version v2.4. I used the older, binary, package for this post.
Tinfoleak options
Tinfoleak comes with a lot of options to retrieve -public- information from a Twitter account. Below are the most important ones.
-t TWEETS_NUMBER, --tweets TWEETS_NUMBER
analyze TWEETS_NUMBER tweets (default: 200)
-i, --info get general information about the user
-s, --sources get the client applications used to publish every
tweet
-f FOLLOWERS_NUMBER, --followers FOLLOWERS_NUMBER
get the last FOLLOWERS_NUMBER followers for the user
-r FRIENDS_NUMBER, --friends FRIENDS_NUMBER
get the last FRIENDS_NUMBER friends for the user
-w WORDS_NUMBER, --words WORDS_NUMBER
get the top WORDS_NUMBER most used words
--conv get user conversations
--sdate SDATE filter the results with SDATE as start date (format:
yyyy-mm-dd)
--edate EDATE filter the results with EDATE as end date (format:
yyyy-mm-dd)
--stime STIME filter the results with STIME as start time (format:
HH:MM:SS)
--etime ETIME filter the results with ETIME as end time (format:
HH:MM:SS)
--hashtags get information about hashtags
--mentions get information about user mentions
--likes LIKES_NUMBER get information about the last LIKES_NUMBER favorites
tweets
--meta get metadata information from user images
--media [D] [no value]: show user images and videos, [D]: download
user images to "username" directory
--social identify user identities in social networks
--geo FILE get geolocation information and generates an output
FILE (KML format)
--top NUMBER get top NUMBER locations visited by the user
Use cases for Tinfoleak
I find the options for listing the client applications used to publish tweet, the top words used and the top hashtags the most interesting information to profile a Twitter user.
For example if you see that the client application has a high percentage for “Twitter via web” then you might attempt phishing attempts to lure the user into accessing a fake site impersonating Twitter.com.
Additionally the top words and hashtags show the content that is relevant to the user, this is good information for creating targeted phishing campaigns.
Note that for properly profiling a user you can use two approaches:
- Globally, see what’s of most interest to a user in general;
- Specific period, see what topic is currently most trending for a user.
The latter option can be included in Tinfoleak by filtering on date but in general it’s more interesting to focus on global information and not limit yourself to specific information on one time-period.
Testing Tinfoleak
I first ran Tinfoleak on my own Twitter account with these options
tinfoleak -u cudeso --tweets 1000 --social --meta --mentions --hashtags --info --sources -o cudeso.html --likes 100 --words 100 --friends 100 --followers 100
This will generate an HTML file. Note that the output states that the file is in /usr/share/tinfoleak/ but this is not correct. You can find the HTML file in your user home directory. The output of the file is the following
_______ _ __ _ _
|__ __(_) / _| | | | |
| | _ _ __ | |_ ___ | | ___ __ _| | __
| | | | '_ \| _/ _ \| |/ _ \/ _` | |/ /
| | | | | | | || (_) | | __/ (_| | <
|_| |_|_| |_|_| \___/|_|\___|\__,_|_|\_\
Tinfoleak v2.1 [SHA2017 Edition] - "Get intelligence from Twitter"
Vicente Aguilera Diaz. @VAguileraDiaz
Internet Security Auditors
08/07/2017
Looking info for @cudeso:
Getting account information...
OK
Executing operations...
1000 tweets analyzed
OK
Getting followers...
100/100 users analyzed
Output file: /usr/share/tinfoleak/cudeso/followers-20180419/cudeso_followers.txt
Getting friends...
100/100 users analyzed
Output file: /usr/share/tinfoleak/cudeso/friends-20180419/cudeso_friends.txt
Getting favorites...
33/100 tweets analyzed
OK
Generating report...
OK
Your HTML report: /usr/share/tinfoleak/Output_Reports/cudeso.html
Elapsed time: 00:02:38
See you soon!
Output of Tinfoleak
This is a sample of the information contained in the HTML file.
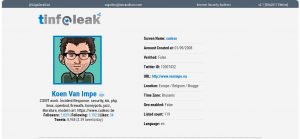
General account information
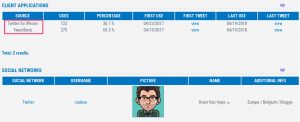
Client applications and social networks
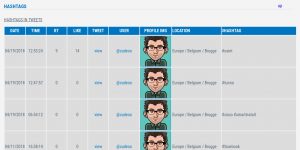
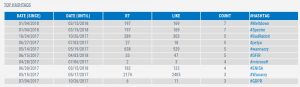
Used hashtags
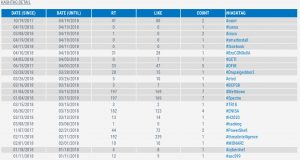
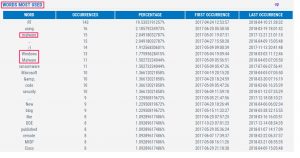
Words most used
Conclusion
Similar to Facebook, people put a lot of information on Twitter that can be used in Phishing campaigns. Tinfoleak also provides the possibility to analyze the
- Last location visited. This returns a KML file that can for example be opened with Google Earth to track the visited locations of a user. It’s not included in this post because I (try to) limit my public location visits.
- Friends & Favorites. This is great information to kick-off a phishing campaign. Impersonating as a friend or someone the user “follows” increases the success-rate.

